Unexpected Vaginal Bleeding After COVID Vaccine, Effects of Aggressively Lowering LDL-C, Potential Benefits of Wastewater Surveillance, Deep Brain Stimulation for Severe Depression, COVID Corner Updates.
The Full Panel meets your TLDR (Too Long; Didn’t Read) needs by delivering the latest medicine & health news in a nutshell. 🥜
Unexpected vaginal bleeding after receiving the COVID-19 vaccination💉

Gist: A study found that women who don't typically menstruate (i.e., post-menopausal or women on contraception) were several times more likely to experience unexpected vaginal bleeding after receiving a COVID-19 vaccination.
Nitty-Gritty: When global COVID-19 vaccine rollouts began, some women reported increased menstrual bleeding after getting the shot.
- Kristine Blix, from the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, and her team used the ongoing "Norwegian Mother, Father, and Child Cohort Study" to examine this issue. They analyzed over 21,000 responses from postmenopausal, perimenopausal, and non-menstruating premenopausal women, many of whom were on long-term hormonal contraceptives.
- Results showed that 252 postmenopausal, 1,008 perimenopausal, and 924 premenopausal women reported unexpected bleeding. About half of each group experienced this within four weeks of receiving a vaccine dose. The risk of unexpected bleeding post-vaccination was highest in premenopausal and perimenopausal women (3-5 times higher) and doubled or tripled for postmenopausal women.
- In October 2022, the European Medicines Agency added heavy menstrual bleeding as a potential side effect for mRNA vaccines, such as Moderna and Pfizer–BioNTech.
Big Picture: While the exact cause of post-vaccination bleeding remains uncertain, recognizing it as a potential side effect is crucial. It can help medical professionals contextualize a patient’s symptoms, especially since unexpected postmenopausal bleeding can indicate serious health issues, like cancer. This research highlights the importance of considering female bleeding patterns in future vaccine and drug trials, shedding light on an often overlooked demographic.
Original source: here.
Potential effects of aggressively lowering LDL-C 🧐

Gist: The American Heart Association (AHA) has released a scientific statement discussing the potential effects of aggressively lowering LDL-C on dementia and hemorrhagic stroke risk.
Nitty-Gritty: Led by Dr. Larry Goldstein from the University of Kentucky, the study titled "Aggressive LDL-C Lowering and the Brain: Impact on Risk for Dementia and Hemorrhagic Stroke" was published in the journal Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.
- The team aimed to determine if aggressive LDL-C lowering could harm the brain, potentially causing cognitive impairment, dementia, or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Their methodology involved literature reviews, published studies, guidelines, authoritative statements, and expert opinions.
- Four key findings emerged:
- LDL-C lowering reduces atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease events in high-risk individuals.
- Though some old studies link LDL-C lowering and cognitive issues, most recent data refute this. More extended studies are still needed.
- There's no significant hemorrhagic stroke risk from statin therapy in patients without prior cerebrovascular disease. Lower LDL-C levels correlate with reduced overall stroke risk.
- Data on hemorrhagic stroke risk from statin use in patients with a previous history of such stroke is limited. PCSK9 inhibitors in these patients also require more study.
Big Picture: While there are concerns about the potential adverse effects of aggressive LDL-C lowering on brain health, current evidence suggests its benefits in reducing cardiovascular risk without significantly increasing the risk for dementia or hemorrhagic stroke. More extended studies are still essential to confirm these findings, especially in specific patient populations.
Original source: here.
Wastewater surveillance may help track other diseases and health risks
Gist: Researchers are leveraging the detection success of COVID-19 in wastewater to monitor a variety of health threats. Wastewater surveillance has expanded significantly during the pandemic and is now being considered for tracking other diseases and health risks.
Nitty-Gritty:
- Before COVID-19, wastewater surveillance mainly targeted specific threats in localized areas, such as opioids in Arizona or polio in Israel.
- The pandemic expanded the reach and significance of wastewater science. Adam Gushgari, an environmental engineer, notes the rapid growth of this subfield, now comprising specialists from diverse areas like microbiology, epidemiology, and chemistry.
- Hundreds of wastewater treatment plants in the U.S. now contribute data to the National Wastewater Surveillance System (NWSS) initiated by the CDC in 2020. Additionally, many more such programs operate globally.
- Beyond COVID-19, researchers are exploring the potential of tracking diseases like the flu, bird flu, and mpox. They are also considering monitoring drug-resistant pathogens and identifying new threats.
- Challenges include validating the data, convincing public officials of its value, and securing sustained funding.
Big Picture: The pandemic ushered in an era of wastewater monitoring on an unprecedented scale, offering a powerful tool for public health surveillance. This method's future depends on continued support from governmental entities, research organizations, and the public, but it holds promise for a broader health impact beyond just COVID-19.
Original source: here.
Deep brain simulation: a surgical treatment for severe depression
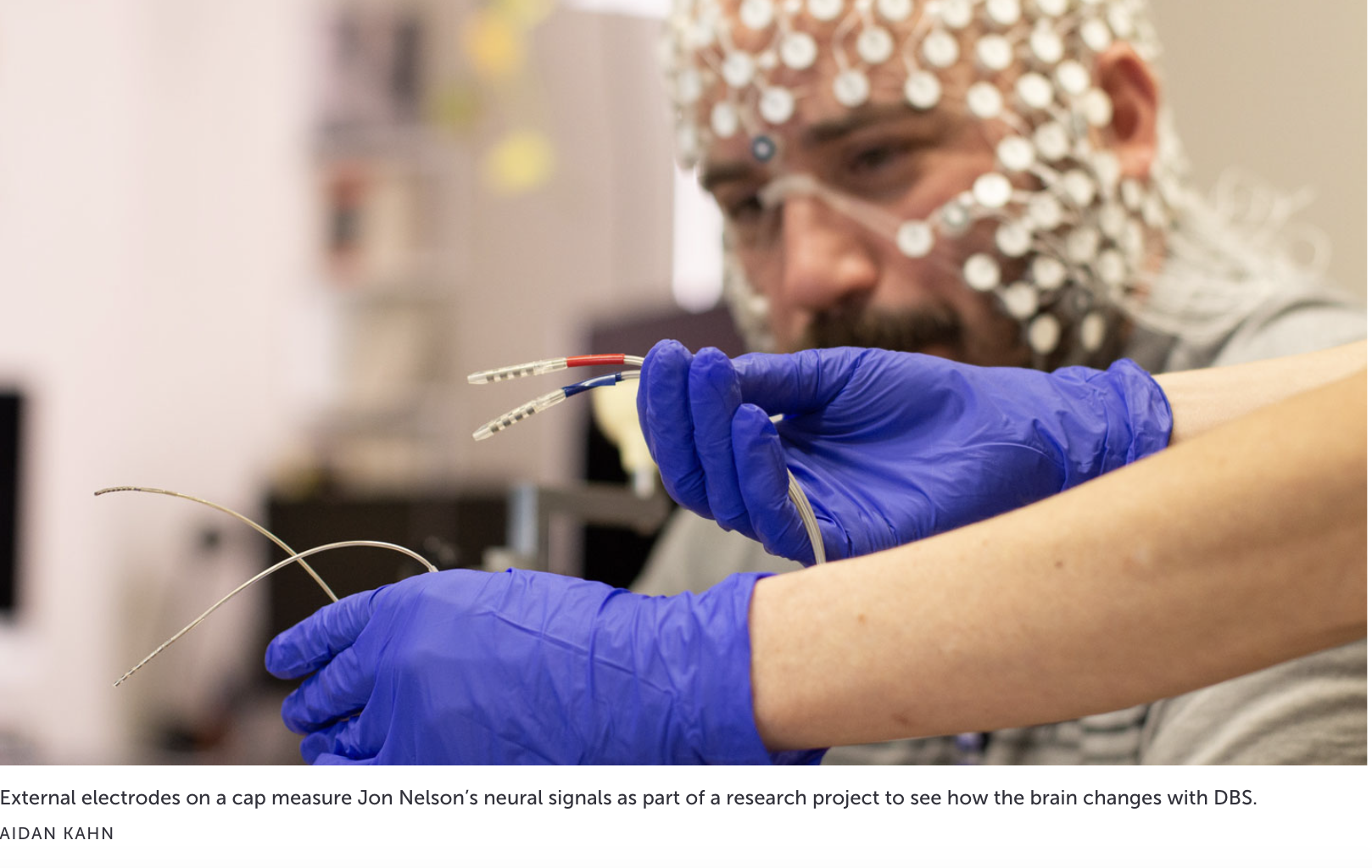

Gist: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment for severe depression that involves implanting electrodes in the brain, connected to battery-powered control units in the chest. While some patients see transformative benefits, they also face challenges like the physical presence of the devices and emotional relearning after surgery.
Nitty-Gritty:
- Patients stated physical discomfort and self-consciousness due to the devices in their chests and wires in their necks.
- There are various post-surgery tasks and protocols, such as charging the device, collecting data, and regular trips to the lab.
- DBS has risks: electrode leads can break, infections, unwanted behavioral changes due to electrical stimulation, and emotional relapses.
- Patients need to distinguish between everyday emotions and clinical depression. Emotional rehab is crucial as they relearn to recognize and tolerate regular feelings.
- DBS doesn’t artificially induce happiness but rather clears the way for natural emotions.
Big Picture: DBS offers hope to those with severe depression but comes with both physical and emotional challenges. The transformative power of the procedure is evident, but it also requires patients to recalibrate their emotional understanding. The treatment challenges our notions of emotional autonomy, pushing us to understand and empathize with those struggling with their emotional landscape.
Original source: here.
COVID Corner: Are face masks back? 😷

Gist: As COVID-19 cases rise in Canada, there's a discussion about the need for increased masking, especially in healthcare settings. Some hospitals are reintroducing stricter masking guidelines while experts suggest that masks should be worn more frequently by the general public to combat the spread of the virus.
Nitty-Gritty:
- Last spring, many health-care settings in Canada lifted universal mask mandates, leading to more relaxed rules in many hospitals.
- As of a recent Tuesday, 2,848 Canadians are hospitalized with COVID-19.
- Many are advocating for the use of quality masks in hospitals to protect patients and visitors.
- 1 in 29 Canadians is estimated to be infected with COVID-19.
- Several hospitals in Ontario have reintroduced more stringent masking requirements.
- Quebec’s Eastern Townships mandated masks in healthcare settings due to rising COVID-19 cases.
- Experts suggest that masks in essential places like pharmacies and grocery stores, particularly to protect vulnerable individuals.
Big Picture: Canada is experiencing a resurgence in COVID-19 cases, sparking renewed concerns over protective measures. While widespread mask mandates might not return, there's a push to emphasize their importance, especially in high-risk areas. Health experts and hospitals are emphasizing the protective benefits of masks, not only against COVID-19 but also against other respiratory viruses. There's a broader call to normalize mask-wearing, particularly to protect the vulnerable and high-risk, and in essential places like pharmacies and grocery stores.
Original source: here.
Updates related to last week's edition of TFP: 🧪
Health Canada has approved Pfizer's latest COVID-19 vaccine, which targets the Omicron XBB.1.5 subvariant, similar to Moderna's recent vaccine. Learn more here.
Interested in previous newsletters or other articles we’ve published? Check them out here at: thefullpanel.com
Got a question for us? Suggestions for content you’d like to see? Feedback? E-mail us at: hello@mail.thefullpanel.com
